electron affinity of k|CALCULLA : Pilipinas The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom to give an anion. In general, elements with the most negative . Just as the symbol nPr represents the number of permutations of n objects taken r at a time, nCr represents the number of combinations of n objects taken r at a time. So in the above example, 3P2 = 6, and 3C2 = 3. Our next goal is to determine the relationship between the number of combinations and the number of permutations in .
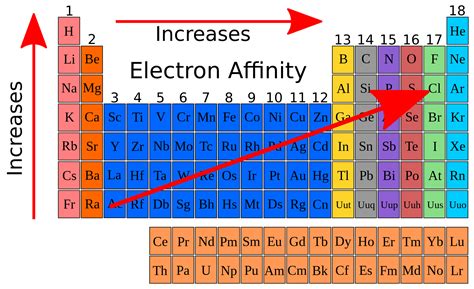
electron affinity of k,Ago 11, 2023 This page deals with the electron affinity as a property of isolated atoms or molecules (i.e. in the gas phase). Solid state electron affinities are not listed here.
Electron affinity is defined as the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion.The electron affinity (Eea) of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron attaches to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form an anion. X(g) + e → X (g) + energyThis differs by sign from the energy change of electron capture ionization. The electron affinity is positive when energy is released on electron capture.
The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom to give an anion. In general, elements with the most negative .electron affinity of kElectron affinity refers to the energy released when an additional electron is attached to a neutral atom to form a singly charged negative ion. Alternatively, it can also be defined as the energy required to detach an electron from the .The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released per mole when an electron is added to a neutral atom. It is the opposite of ionization energy [1-4]. How to Find Electron Affinity. The electron affinity is generally .Chemists define electron affinity as the change in energy, measured in units of kJ/mole, experienced when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. This process creates a negative ion.
Table shows electron affinity (i.e. the amount of energy released when an electron is added to atom) for most of chemical elements.
Electron affinity is a measure of how readily a neutral atom gains an electron. Electron affinity (Eea) is the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the .The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form a negative ion \[X_{(g)} + e^− \rightarrow X^−_{(g)} + energy\] Z Element Name Electron affinity (eV) Electron affinity (kJ/mol) 1: 2 D: Deuterium: 0.754 59(8) 72.807(8) 1: 1 H:The electronic affinity is amount of energy, that is released during the attachment of the electron to the neutral atom. As a result of such attachment, a negative ion (anion) is formed. Electron affinity is related to electronegativity of elements.Simply speaking, the greater the affinity of electrons, the more eagerly the atoms of a given element join electrons to form .
Definition of Electron Affinity. Electron affinity is a quantitative measurement of the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom. The more negative the electron affinity value, the higher the electron affinity and the more easily an electron is added to an atom. Electron affinity can be either positive or .electron affinity of k CALCULLA The electron affinity of K is 48 kJ/mol. Write the equation for which this is the energy change. Electron Affinity: Electron affinity is the accompanying amount of energy released from the addition of an extra electron to a neutral gaseous atom. Atoms are able to capture electrons if their nuclear forces are not completely screened by . This affinity is known as the second electron affinity and these energies are positive. Electron affinity can be either positive or negative value. The greater the negative value, the more stable the anion is. Although affinity varies greatly across the periodic table, some patterns emerge. Generally, the elements on the right side of the . What is Electron Affinity? Electron affinity is the amount of energy change (ΔE) that occurs when an electron is added in the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom. In simple words, when the electron is added to the neutral atom, the energy is either absorbed or released. This amount of energy change (ΔE) is the electron affinity of .
What is Electron Affinity? Chemists define electron affinity as the change in energy, measured in units of kJ/mole, experienced when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. This process creates a negative ion. This process differs from electronegativity, which we define as the ability of an atom to attract an electron toward itself.
Neither K nor Ca "wants" to ionize. Both ionization energies are endothermic. This question refers to eelctron affinity, which is gaining an electron. K has a more exothermic electron affinity because the electron gained fills the 4s orbital. In Ca the electron goes to 3d. The energy gap between 4s and 3d is enough to make the process barely .Electronegativity is a function of: (1) the atom's ionization energy (how strongly the atom holds on to its own electrons) and (2) the atom's electron affinity (how strongly the atom attracts other electrons). Both of these are properties of the isolated atom.An element that is will be highly electronegative has:. a large (negative) electron affinity
The first ionization energy for sodium is one and one-half times larger than the electron affinity for chlorine. Na: 1st IE = 495.8 kJ/mol. Cl: EA = 328.8 kJ/mol. Thus, it takes more energy to remove an electron from a neutral sodium atom than is given off when the electron is picked up by a neutral chlorine atom.
CALCULLA Electron Affinities of the Main-Group Elements* The electron affinity is a measure of the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form a negative ion. For example, when a neutral chlorine atom in the gaseous form picks up an electron to form a Cl- ion, it releases an energy of 349 kJ/mol or 3.6 eV/atom.

Electron Affinity of Noble Gases. Next to the right, we have the noble gases which are characterized by endothermic electron affinity because there are no vacant p orbitals in their valence shell, not even with one electron in it, and . The difference in energies gave the vertical electron affinity in the solid state. Single point calculation of the molecule is also done without PCM, which gives the gas phase electron affinity. Ionization potentials in the solid state were also determined using the method reported earlier [9]. Singlet optical transition energy was calculated .

For the gaseous reaction, K + F → K + F −, Δ H was calculated to be 19 kcal under conditions where the cations and anions were prevented by electrostatic separation from combining with each other. The ionization potential of K is 4.3 eV atom. The electron affinity of F will be:
Electron Affinity (V) 4.05: 4.0: 4.07: Energy Gap at 300K (eV) 1.12: 0.66: 1.424: . , electrons: 1500: 3900: . 0.31: 0.35: Thermal Conductivity at 300 K (W/cm-degC) 1.5: 0.6: 0.46: Thermal Diffusivity (cm 2 /sec) 0.9: 0.36: 0.24: Vapor Pressure (Pa) 1 at 1650 deg C; 10-6 at 900 deg C: 1 at 1330 deg C; . The K+ ion would more likely to have the higher electron affinity value. The ion has a full valence shell, so a lot more energy would be required to break that stable state that it would be to add another electron to a neutral K ion (which then would have a filled 4s orbital). Top. 804994652Ionization Energies of s- and p-Block Elements. Ionization energies of the elements in the third row of the periodic table exhibit the same pattern as those of \(Li\) and \(Be\) (Table \(\PageIndex{2}\)): successive ionization energies increase steadily as electrons are removed from the valence orbitals (3s or 3p, in this case), followed by an especially large increase in .Electron affinity (the energy associated with forming an anion) is more favorable (exothermic) when electrons are placed into lower energy orbitals, closer to the nucleus. Therefore, electron affinity becomes increasingly negative as we move left to right across the periodic table and decreases as we move down a group. For both IE and electron .
electron affinity of k|CALCULLA
PH0 · What Is Electron Affinity?
PH1 · Electron affinity (data page)
PH2 · Electron affinity
PH3 · Electron Affinity: Definition, Chart & Trend in Periodic Table
PH4 · Electron Affinity: Definition, Chart & Trend in Periodic
PH5 · Electron Affinity Trend and Definition
PH6 · Electron Affinity Chart (Labeled Periodic table + List)
PH7 · Electron Affinity
PH8 · CALCULLA
PH9 · 7.5: Electron Affinities